In recent years, the debate between hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (HFCVs) and electric vehicles (EVs) has gained significant attention. While EVs, championed by figures like Elon Musk, have dominated the market, hydrogen fuel cell technology continues to have its proponents and potential applications. In this blog post, we will delve into the Hydrogen Cars in India, advantages and disadvantages of hydrogen cars, shed light on the reasons behind their limited market success, and discuss the potential future of hydrogen as a clean energy source.
How do Hydrogen Cars Work?
Hydrogen cars consist of several key components that work together to produce sustainable transportation:
-
Fuel Cell Stack: This is the heart of a hydrogen car. The fuel cell stack contains multiple individual fuel cells that combine hydrogen with oxygen from the air to produce electricity.
-
Hydrogen Tank: Hydrogen is stored in high-pressure tanks within the vehicle. The tanks are designed to safely store hydrogen gas until it is needed.
-
Electric Motor: The electricity generated by the fuel cell stack powers the car’s electric motor, enabling it to move.
-
Battery Pack: Hydrogen cars also include a small battery pack that assists the electric motor during peak power demands or during regenerative braking.
Green Hydrogen Cars in India:
1. Toyota Mirai: The Mirai is a midsize sedan produced by Toyota. It features a fuel cell stack that converts hydrogen into electricity to power the vehicle. It has a range of around 300 miles (483 kilometers) on a full tank of hydrogen.

2. Hyundai Nexo: The Nexo is a compact SUV manufactured by Hyundai. It utilizes a fuel cell system to generate electricity, providing a range of approximately 380 miles (612 kilometers). The Nexo also has advanced driver-assistance systems and other innovative features.

3. Honda Clarity Fuel Cell: The Clarity Fuel Cell is a midsize sedan offered by Honda. It runs on hydrogen and has a range of around 360 miles (579 kilometers). The vehicle features advanced safety technologies and a spacious interior.

4. Audi A7 h-tron quattro: The A7 h-tron quattro is a hydrogen fuel cell vehicle prototype developed by Audi. It combines a fuel cell stack with a battery pack to provide an all-electric driving experience. The A7 h-tron quattro offers a range of approximately 310 miles (500 kilometers) on hydrogen alone.

5. BMW i Hydrogen NEXT: The i Hydrogen NEXT is a hydrogen fuel cell vehicle concept from BMW. It is based on the BMW X5 SUV and features a fuel cell system developed in collaboration with Toyota. The vehicle aims to combine the benefits of hydrogen with BMW’s electric drivetrain expertise.

Advantages of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles:
- No Range Anxiety: One of the key advantages of HFCVs is their ability to be refuelled quickly, similar to vehicles powered by internal combustion engines (ICE). Unlike EVs, which often require longer charging times, HFCVs can be filled with hydrogen in a matter of minutes, eliminating range anxiety for drivers.
- Lightweight and Efficient: Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles tend to be lighter than EVs due to the lower weight of their energy storage systems. This characteristic enhances their overall energy efficiency and contributes to improved performance.
- Potential for Long-Distance Travel: Hydrogen’s high energy density makes it an appealing option for applications such as buses, trucks, ships, and potentially aircraft. The ability to travel long distances without frequent refuelling is a significant advantage for these industries.
Challenges and Limitations of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles:
- Limited Infrastructure: The lack of a widespread hydrogen refueling infrastructure is one of the primary challenges facing the adoption of HFCVs. Building an extensive network of refueling stations would require significant investments and time, hindering the mass adoption of hydrogen cars.
- Cost and Production: Hydrogen production methods, particularly green hydrogen generated through electrolysis, require electricity generated from renewable resources. Currently, the world’s reliance on fossil fuels limits the production of truly “green” hydrogen. Additionally, the cost of hydrogen production, storage, and transportation remains relatively high.
- Efficiency and Energy Loss: The conversion of hydrogen into electricity in fuel cells involves a series of energy conversions, leading to energy losses at each step. This lower efficiency, compared to direct electricity transmission in EVs, is a drawback of HFCVs.
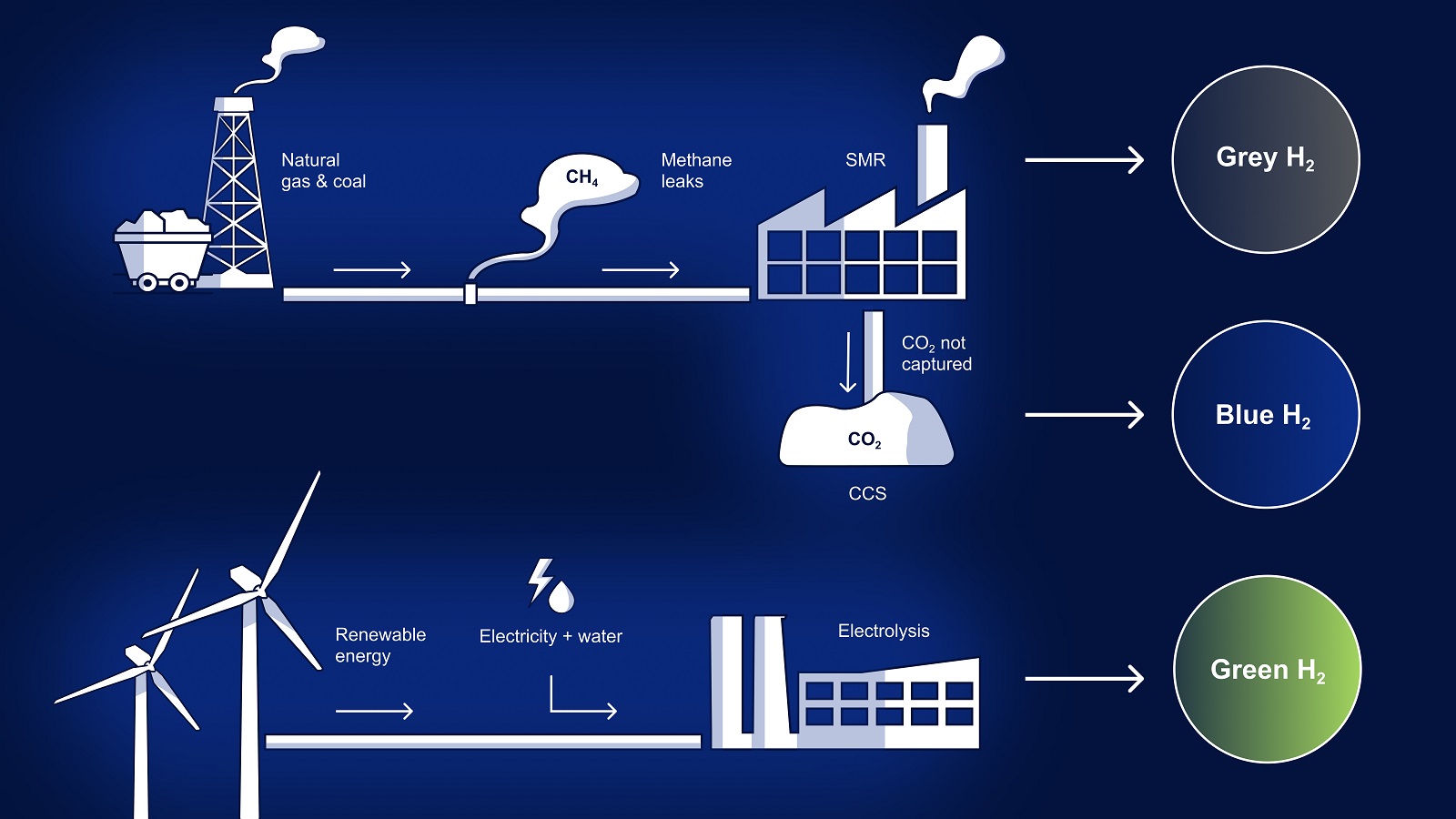
What is Green, gray, and blue hydrogen?
Green, grey, and blue hydrogen are different classifications that refer to the methods used to produce hydrogen and their associated carbon emissions. Here’s a brief explanation of each type:
1. Green hydrogen:
Green hydrogen is produced through a process called electrolysis, where water (H2O) is split into hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) using electricity from renewable sources like solar or wind power. Since the electricity used is generated from renewable energy, green hydrogen production has no direct carbon emissions and is considered environmentally friendly.
2. Grey hydrogen:
Grey hydrogen is produced from natural gas through a process called steam methane reforming (SMR). It is the most common method of hydrogen production today. During SMR, natural gas reacts with high-temperature steam, resulting in the release of hydrogen and carbon dioxide (CO2). Grey hydrogen is considered to have high carbon emissions since it relies on fossil fuels.
3. Blue hydrogen:
Blue hydrogen is produced similarly to grey hydrogen through steam methane reforming but with an additional step called carbon capture and storage (CCS). CCS captures the carbon dioxide emitted during the hydrogen production process and stores it underground, preventing it from entering the atmosphere. By implementing CCS technology, blue hydrogen aims to reduce its carbon footprint and lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to grey hydrogen.
It’s important to note that the terms “green,” “grey,” and “blue” are used to categorize the carbon intensity of hydrogen production processes and do not directly refer to the physical properties or composition of hydrogen itself.
Why Have Hydrogen Cars Struggled in the Market?
Despite their advantages, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles have faced significant challenges in gaining widespread market acceptance. Some key reasons include:
- Limited Renewable Energy Generation: In many countries, including the United States, a substantial portion of electricity generation still relies on non-renewable sources. This hampers the potential for truly green hydrogen production and weakens the environmental case for HFCVs.
- Lack of Infrastructure: The scarcity of hydrogen refueling stations makes it inconvenient for potential buyers to own and operate hydrogen cars. This lack of infrastructure creates a barrier to entry, leading to limited demand and slow market growth.
- Cost and Competition: The relatively high cost of hydrogen fuel cell technology, coupled with the success and rapid growth of EVs, has made it difficult for HFCVs to compete in the market. Established EV manufacturers like Tesla have gained significant market share, overshadowing the adoption of hydrogen cars.
The Future of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles in India:
Despite their current challenges, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles still hold promise in certain sectors and applications. Ongoing research and development efforts aim to address the limitations and promote the wider adoption of HFCVs. Advancements in renewable energy generation, infrastructure development, and cost reduction could potentially reshape the automotive industry’s landscape in the future. These were some of the facts which Elon Musk consider hydrogen fuel cell vehicle to be a stupid idea on one side. But the side, Shri Nitin Gadkari wants to make India a global leader in terms of production of green hydrogen. And that’s why the big players like Adani Group have started. Marching towards green hydrogen. Nitin Gadkari wants the production of hydrogen through biowaste and savage water apart from electrolysis. Here chemical reactions would be used for the production of hydrogen gas.
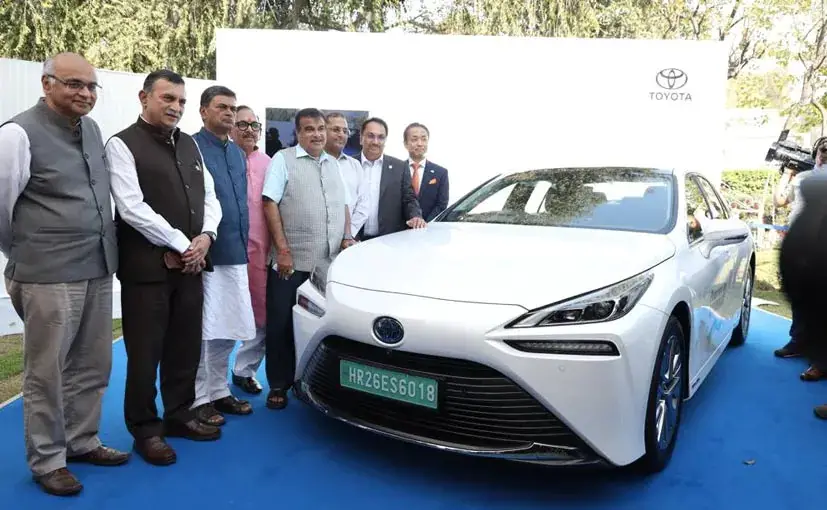
Currently, there are limited options for hydrogen fuel cell vehicles in the Indian market. Toyota has launched a pilot project to test their Mirai FCEV in collaboration with the Indian government’s testing agency, iCAT. The Mirai is a hydrogen-powered car with a design that resembles conventional vehicles rather than a futuristic spaceship. This project aims to evaluate the performance and suitability of the Mirai in Indian conditions. While the availability of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles in India is still limited, the pilot project indicates a growing interest in hydrogen technology in the country.

FAQ:
Q 1: Are hydrogen cars safe?
Yes, hydrogen cars are designed with safety in mind. The hydrogen tanks undergo rigorous testing to ensure they can withstand extreme conditions and prevent leaks. Additionally, hydrogen is lighter than air and disperses rapidly, further minimizing safety risks.
Q 2: Is hydrogen readily available in India?
While hydrogen infrastructure is currently limited in India, efforts are underway to establish hydrogen production and refueling facilities. As renewable energy gains traction, hydrogen production is expected to become more accessible and widespread.
Q 3: Are hydrogen cars, expensive?
Hydrogen cars are currently more expensive than traditional gasoline or electric vehicles. However, as technology advances and economies of scale come into play, the cost is expected to decrease, making hydrogen cars more affordable in the future.
Q 4: How does hydrogen production impact the environment?
The environmental impact of hydrogen production depends on the method used. If hydrogen is produced through electrolysis using renewable energy sources, it has a minimal carbon footprint. However, if hydrogen is derived from fossil fuels, such as natural gas, it can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
Q 5: Are there hydrogen fueling stations in India?
While the number of hydrogen fueling stations in India is currently limited, plans are underway to expand the infrastructure. Several pilot projects and collaborations aim to establish a network of hydrogen fueling stations across the country.
Q 6: Can hydrogen cars compete with electric vehicles?
Hydrogen cars and electric vehicles each have their advantages and limitations. While electric vehicles have a more developed infrastructure and are currently more widely adopted, hydrogen cars offer faster refueling times and longer driving ranges. The competition between the two technologies will likely drive innovation and lead to advancements in both sectors.
Q 7:how do hydrogen cars refuel
Hydrogen cars are refueled by connecting a special nozzle to the car’s fueling receptacle and pumping hydrogen gas into the tank at a hydrogen refueling station. Same as refueling CNG, and LPG gas in cars.
Conclusion:
While there are challenges associated with hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, it is important to recognize that both EVs and hydrogen-powered solutions have their strengths and weaknesses. The success of each technology depends on addressing issues such as sustainable energy sources, infrastructure development, cost-effectiveness, and market demand. As the world moves towards a more sustainable future, both electric vehicles and hydrogen-powered solutions will likely play significant roles in shaping the transportation industry.






